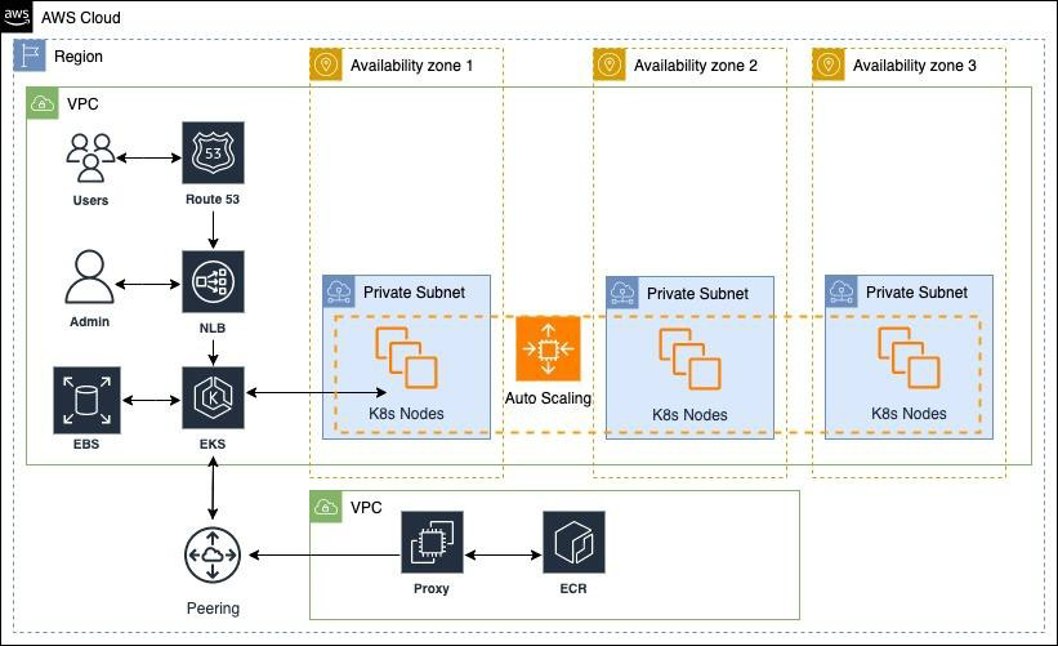
Air Gap Architecture
Cogynt may also be deployed in an air gap (meaning that it is not accessible via the Internet) as either a multi-AZ or single-AZ architecture. In this architecture, the internet and NAT gateways responsible for internet access are removed.
note
Air gap deployments support both multi-AZ and single-AZ architecture. For brevity, only the multi-AZ architecture setup is delineated here.
For more information about single-AZ architecture, see Single-AZ Architecture.
AWS
The components of an air gap AWS multi-AZ configuration are as follows:
- An internet gateway allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
- A network load balancer distributes web traffic across an automatically-scaling group of Amazon EC2 instances (or a single instance for single-AZ setups).
- Amazon EC2 instances access shared data in an Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) file system using mount targets in each AZ.
- The Amazon EBS provides access to shared, unstructured data such as config, themes, and plugins.
- Peering allows VPCs to communicate.
- A proxy and ECR allow Cogynt to be installed and updated.
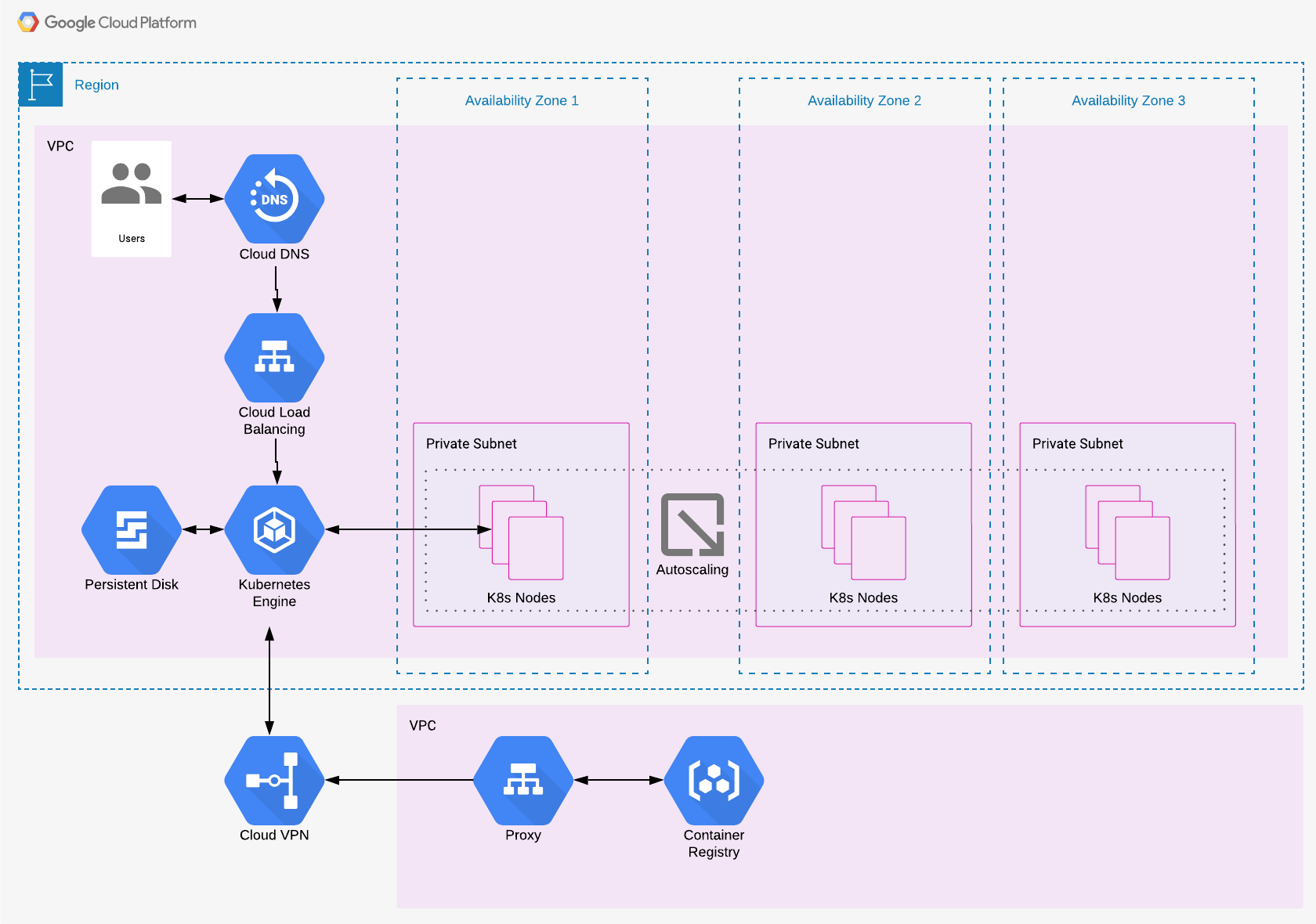
GCP
The components of an air gap GCP multi-AZ configuration are as follows:
- An internet gateway allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
- A network load balancer distributes web traffic across an automatically-scaling group of VM instances (or a single instance for single-AZ setups).
- VM instances access shared data in a persistent disk file system using mount targets in each AZ.
- The persistent disk provides access to shared, unstructured data such as config, themes, and plugins.
- Peering allows VPCs to communicate.
- A proxy and container registry allow Cogynt to be installed and updated.